Efficient Mobile Robot Communication using Fuzzy-driven CH Selection and CH Chaining-Based Relaying
Problem Definition
From the literature survey conducted, it is evident that the domain of mobile robot swarm-based communication is gaining significant attention from researchers due to its applications in various fields such as searching and field communication. However, several challenges exist that hinder the establishment of a reliable and robust infrastructure in the realm of mobile robotics. While existing research primarily focuses on energy factors of neighboring nodes for selecting the Cluster Head (CH) in the network, it is clear that other crucial factors are being overlooked. Additionally, though the concept of relaying has been introduced by some researchers, its efficiency in the network has not been optimized, leading to delays in data transmission and decision-making by the mobile robots. Moreover, the mobility of the sink node could potentially impede the data transmission process.
To address these limitations and problems, a new and improved methodology needs to be developed to enhance the performance and efficiency of mobile robot swarm-based communication systems.
Objective
The objective of this study is to develop an improved methodology using Fuzzy Logic System to enhance the performance and efficiency of mobile robot swarm-based communication systems. This methodology aims to address the limitations in existing systems by focusing on reducing energy consumption, improving Cluster Head (CH) selection, and optimizing data relaying from sensor nodes to the sink node. By incorporating fuzzy logic to consider communication distance, connection requests, and residual energy of nodes, the proposed model aims to make efficient decisions for CH selection. Additionally, by enhancing the relaying mechanism, data transmission from sensor nodes to the sink node can be improved. Overall, the objective is to establish a reliable and robust infrastructure for mobile robot swarm-based communication systems.
Proposed Work
In order to overcome the limitations of existing mobile robot communication systems, an improved and efficient model that is based on Fuzzy Logic System (FLS) is proposed in this paper. The main objective of the proposed strategy is to reduce energy consumption of nodes so that overall lifespan of network is enhanced. Basically, the proposed approach works improves the performance of mobile robot system at two stages, i.e. CH selection and relaying data from sensor nodes to sink node.
For selecting the efficient CH in the network, the proposed model employs fuzzy logic system (FLS) which takes three inputs and generates a single outcome. The three important parameters used in FLS are Communication Distance between sensor and sink node (Dcomm), Connection requests (Creq) and residual energy of nodes (Eres) of the node. These models are processed by the knowledge base module and finally a single output “prob” is generated. One of the key goals of adopting fuzzy systems is to reduce the complexity brought on by the use of straightforward mathematical models. The relaying mechanism has been improved in the second phase of the suggested paradigm.
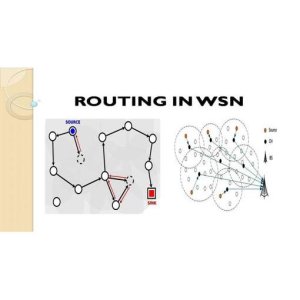
The technique of transferring data from the sensor node to the sink node or BS is decided by the relaying procedure. In the proposed work, data is sent to the sink node via the CH node using the CH node relaying mechanism. This will make it easier for the proposed approach to choose the relaying path quickly so that the data can be delivered to the sink within its mobility step time.
Application Area for Industry
The project on mobile robot swarm-based communication can be applied in various industrial sectors such as agriculture, warehouse management, and surveillance. In agriculture, the use of mobile robots can aid in tasks such as crop monitoring, watering, and pest control. The proposed solutions of improved CH selection and relaying data can help in optimizing the communication network within agricultural fields, ensuring efficient data transmission and reduced energy consumption of nodes. In warehouse management, mobile robots can be utilized for inventory tracking, material handling, and order fulfillment. The application of fuzzy logic systems in CH selection can enhance the efficiency of robots in navigating through the warehouse and relaying data to the central system.
In the surveillance industry, mobile robots can be deployed for monitoring and patrolling in areas where human access is limited. The proposed solutions can address the challenges of selecting optimal CH nodes and efficient data relaying, ensuring real-time data transmission and improved surveillance operations. Overall, implementing the proposed solutions in different industrial domains can lead to increased productivity, reduced operational costs, and enhanced overall performance of mobile robot systems.
Application Area for Academics
The proposed project on mobile robot swarm-based communication utilizing fuzzy logic system can significantly enrich academic research, education, and training in the field of robotics and communication systems. By addressing the challenges related to CH selection and data relaying, the project offers a new and efficient method to improve the performance of mobile robot systems.
This research has the potential to contribute to innovative research methods and simulations within educational settings by providing a practical application of fuzzy logic systems in the context of mobile robotics. The use of FLS for CH selection and relaying data can be a valuable learning tool for students and researchers interested in exploring advanced techniques in communication networks. The proposed model can serve as a practical example of how fuzzy logic can be applied to optimize network performance and energy efficiency in mobile robot systems.
Researchers, MTech students, and PhD scholars in the field of robotics and communication systems can benefit from this project by utilizing the code and literature to enhance their own work. The algorithms used in the project, such as fuzzy logic and relaying routing, can be implemented in other research projects to improve network performance and energy efficiency.
In terms of future scope, the project can be extended to further explore the potential applications of fuzzy logic systems in mobile robot communication, as well as to optimize other aspects of network performance. Additionally, the proposed model can be tested and validated through real-world experiments to demonstrate its effectiveness in practical scenarios. Overall, the project offers a valuable contribution to academic research and education in the field of mobile robot swarm-based communication.
Algorithms Used
The proposed model in this project employs Fuzzy Logic System (FLS) to improve the performance of mobile robot communication systems. FLS is used for CH selection based on parameters like communication distance, connection requests, and residual energy of nodes. This helps in reducing energy consumption and enhancing network lifespan. In the second phase, the relaying routing algorithm is used to efficiently transfer data from sensor nodes to the sink node via the selected CH node. This approach helps in quick and effective data delivery to the sink within the specified mobility step time.
These algorithms work together to achieve the project's objectives of enhancing accuracy and improving efficiency in mobile robot communication systems.
Keywords
SEO-optimized keywords: wireless sensor networks, route optimization, CH election, network lifetime, energy efficiency, network performance, routing protocols, network longevity, network scalability, optimization algorithms, energy-aware routing, network management, network protocols, cluster-based routing, network coverage, mobile robot swarm-based communication, Fuzzy Logic System (FLS), CH selection, relaying, Communication Distance, Connection requests, residual energy, knowledge base module.
SEO Tags
mobile robot swarm-based communication, mobile robotics, CH selection, fuzzy logic system, node energy consumption, sensor nodes, sink node, relaying mechanism, network infrastructure, communication systems, network optimization, route optimization, network lifetime, energy efficiency, routing protocols, optimization algorithms, energy-aware routing, network management, cluster-based routing, network coverage, wireless sensor networks, network scalability, research methodology.
| Shipping Cost |
|
No reviews found!
















































No comments found for this product. Be the first to comment!