Efficient Fuzzy Logic based Cluster Routing Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks
Problem Definition
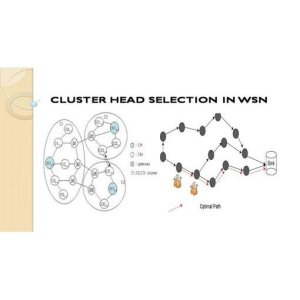
Wireless sensor networks play a crucial role in monitoring physical or environmental conditions by utilizing autonomous sensors distributed in a spatial manner. These networks function by cooperatively transmitting data to a centralized location. However, the dynamic nature and openness of these networks present various uncertainties and challenges. One key limitation identified in the literature is the lack of a defined routing system from the cluster head (CH) to the sink. Additionally, the process of selecting the CH among nodes needs to be streamlined and based on specific statistics.
Addressing these issues is crucial for optimizing the performance and efficiency of wireless sensor networks in order to ensure accurate and timely data transmission.
Objective
The objective is to address the limitations in wireless sensor networks related to the lack of a defined routing system from the cluster head to the sink and inefficient selection of cluster heads. The proposed work aims to introduce an intelligent fuzzy logic system for selecting cluster heads in WSNs and improving transmission efficiency under multi-link interference scenarios. By focusing on transmission from cluster heads to the sink, the research project aims to enhance network parameters, node energy, and centrality through the implementation of energy dissipation and dynamic channel assignment. Through this approach, the goal is to optimize the performance and efficiency of wireless sensor networks for accurate and timely data transmission.
Proposed Work
The problem of selecting cluster heads in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) has been identified due to the lack of an efficient routing algorithm from cluster heads to the sink. Existing research has focused on the transmission from nodes to cluster heads without addressing the further routing of data. The proposed work aims to introduce an intelligent fuzzy logic system for selecting cluster heads in WSNs. By utilizing a source routing protocol based on-demand routing and dynamic channel assignment, the goal is to improve transmission efficiency under multi-link interference situations. This approach will help in maximizing the efficiency of links along the selected path, reducing average congested end-to-end delay, and increasing the packet delivery ratio by considering energy and coverage requirements.
By integrating fuzzy logic for cluster head selection and working on transmission from cluster heads to the sink, this research project seeks to enhance the parameters at both transmission stages. The methodology involves defining network parameters, evaluating node energy and centrality, designing a fuzzy logic system for selecting cluster heads, and implementing energy dissipation to achieve the project's objectives.
Application Area for Industry
This project can be applied in various industrial sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, and healthcare where wireless sensor networks are utilized for monitoring physical or environmental conditions. The proposed solutions address challenges related to inefficient transmission from cluster heads to sink, undefined routing paths, and lack of effective cluster head selection criteria. By introducing a source routing protocol and dynamic channel assignment, the project aims to improve transmission efficiency and reduce congested end-to-end delay, resulting in enhanced monitoring and control of sensor activities. The use of fuzzy logic for cluster head selection criteria will provide a more accurate and reliable method for nodes to decide their role within the network, leading to optimized energy consumption and improved data transmission.
The benefits of implementing these solutions are significant across different industrial domains.
In agriculture, for example, the project can help optimize irrigation systems by providing real-time data on soil conditions and crop health. In manufacturing, it can enhance supply chain management by improving inventory tracking and equipment monitoring. In healthcare, it can enable remote patient monitoring and medical equipment maintenance. Overall, by addressing the uncertainties in wireless sensor networks and improving the efficiency of data transmission, this project can bring about improved operational performance, cost savings, and enhanced decision-making capabilities in various industries.
Application Area for Academics
The proposed project can significantly enrich academic research, education, and training in the field of wireless sensor networks. By introducing a source routing protocol based on-demand routing and dynamic channel assignment, researchers and students can explore innovative research methods to improve transmission efficiency under multi-link interference situations. This project also addresses the issue of uncertain cluster head selection by replacing the traditional approach with fuzzy logic, which enhances the cluster head selection criterion.
The relevance of this project lies in its potential applications for researchers, MTech students, and PhD scholars in the field of wireless sensor networks. By utilizing the code and literature provided by this project, researchers can explore new avenues for designing routing algorithms from cluster heads to the sink, thereby improving the overall performance of the network.
MTech students can use this project to gain hands-on experience with fuzzy logic systems and energy dissipation mechanisms in wireless sensor networks, while PhD scholars can leverage the methodology proposed in this project for their advanced research work.
In educational settings, this project can be used to teach students about the importance of efficient data transmission in wireless sensor networks and the role of cluster head selection in network optimization. By simulating different scenarios and implementing the proposed fuzzy logic system, students can gain a deeper understanding of network parameters and energy management strategies.
Overall, the proposed project has the potential to enhance academic research, education, and training by providing a platform for exploring innovative research methods, simulations, and data analysis in the context of wireless sensor networks. The field-specific researchers, MTech students, and PhD scholars can benefit from the code and literature of this project to advance their work and contribute to the ongoing research in this domain.
Future scope: In the future, this project can be further extended to include more advanced algorithms for energy optimization, adaptive routing, and self-organizing networks. By incorporating machine learning techniques and advanced optimization algorithms, researchers can explore new ways to improve the performance and efficiency of wireless sensor networks. Additionally, the project can be expanded to cover other emerging technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) and smart grid systems, opening up new avenues for research and innovation in the field of wireless communication.
Algorithms Used
Fuzzy Logic is used in this project to improve the cluster head selection criterion and enhance the transmission efficiency of data packets in a wireless sensor network. The algorithm evaluates network parameters, node energy, centrality, and adjacency metrics using fuzzy inference models to determine the maximum chance of a node becoming a cluster head. By implementing energy dissipation strategies based on fuzzy logic, the project aims to optimize the performance of the network by selecting the most suitable nodes as cluster heads and improving the overall transmission process from nodes to cluster heads and from cluster heads to the sink.
Keywords
SEO-optimized keywords: Wireless Sensor Networks, Sensor Nodes, Environmental Monitoring, Network Topology, Bi-directional Networks, Cluster Heads, Routing Algorithm, Source Routing Protocol, Dynamic Channel Assignment, Multi-link Interference, Transmission Efficiency, Congested End-to-End Delay, Packet Delivery Ratio, Energy Consumption, Coverage Requirement, Fuzzy Logic, Cluster Head Selection, Data Transmission, Network Parameters, Initial Energy, Centrality, Adjacency Metric, Fuzzy Inference Model, Energy Dissipation.
SEO Tags
Wireless Sensor Networks, Nodes, Fuzzy Logic, Cluster Head Selection, Energy Efficiency, Source Routing Protocol, Dynamic Channel Assignment, On-Demand Routing, Data Transmission, Multi-Link Interference, Fuzzy Inference Model, Energy Dissipation, Network Parameters, Centrality, Adjacency Metric, Routing Algorithm, PHD Research, MTech Research, Research Scholar, Data Transmission Efficiency, Network Topology, Sensor Activity Control, Statistic for Node Selection, Leach Protocol, Channel Efficiency, Transmission Optimization, Energy Consumption Model.
| Shipping Cost |
|
No reviews found!















































No comments found for this product. Be the first to comment!