Solar-Powered Energy Optimization using Hybrid Control System and Genetic Algorithm Tuning
Problem Definition
The main focus of this research project is on addressing the limitations and inefficiencies within solar power systems, specifically related to the resistance generated by the VI characteristics of solar panels. These resistances lead to a significant loss of power output, highlighting the need for an optimized Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) system. Without an efficient MPPT system in place, solar power systems are unable to fully utilize the power generated by the photovoltaic cells, resulting in reduced efficiency in converting sunlight into electricity. Thus, the key challenge lies in maximizing the output of solar power systems by implementing a more effective MPPT system that can overcome the limitations posed by resistance and improve the overall efficiency of converting solar energy into electricity. The necessity of this project stems from the critical need to harness the full potential of solar energy as a sustainable and renewable power source, thereby addressing the pressing environmental concerns related to energy consumption and climate change.
Objective
The objective of this research project is to develop and implement an optimized Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) system for solar power systems. By utilizing a hybrid system combining P&O and PID controllers, along with genetic algorithms to set PID controller gain values, the aim is to maximize power extraction from solar panels and overcome the inefficiencies caused by resistance in the VI characteristics. Through conducting various case studies and simulations using MATLAB, the project seeks to design a more efficient MPPT system that can enhance the overall conversion of sunlight into electricity, ultimately increasing the output and performance of solar power systems.
Proposed Work
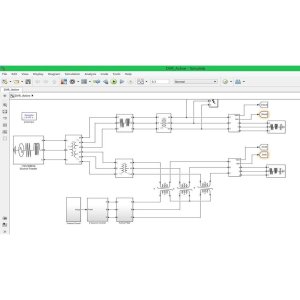
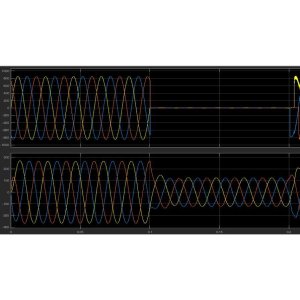
The proposed work aims to address the inefficiencies in solar power systems by implementing an optimized Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) system. By utilizing a hybrid system that combines P&O and PID controllers, the project seeks to maximize power extraction from solar panels. The use of a genetic algorithm to set gain values in the PID controller enhances the system's performance. Various case studies will be conducted to compare the system's performance under different conditions such as varying levels of electric vehicle battery charge and solar panel irradiance. Ultimately, the goal is to design a more efficient MPPT system that can significantly improve the conversion of sunlight into electricity.
The choice of MATLAB as the software for this project ensures accurate simulation and analysis of the proposed system.
Application Area for Industry
This project can be used in various industrial sectors such as renewable energy, power generation, and electric vehicles. By implementing the proposed solutions for maximizing the output of solar power systems through efficient MPPT systems, industries can address the challenge of minimizing power loss due to resistance in solar panels. The use of hybrid controllers and genetic algorithms can significantly improve the efficiency of converting sunlight into electricity, allowing industries to harness more power from their solar systems. This enhanced efficiency will not only result in cost savings for businesses but also contribute to reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainability in different industrial domains.
Application Area for Academics
The proposed project on maximizing the output of solar power systems through a hybrid MPPT system has great potential to enrich academic research, education, and training in various ways.
In terms of academic research, this project delves into the optimization of solar power systems utilizing advanced algorithms such as the P&O method, PID controller, and Genetic Algorithm. Researchers in the field of renewable energy, electrical engineering, and algorithm optimization can explore the effectiveness of these methods and further enhance them to improve the overall efficiency of solar power systems.
For educational purposes, the project provides a practical application of theoretical concepts taught in classrooms. Students can learn about the functioning of solar power systems, MPPT algorithms, and controller tuning through hands-on experience with MATLAB simulations.
This project can serve as a valuable educational tool for engineering students interested in renewable energy technologies.
Moreover, the project offers training opportunities for students and professionals in the field of renewable energy. By working on the simulation and analysis of the hybrid MPPT system, individuals can gain practical skills in designing, testing, and optimizing solar power systems. This hands-on training can prepare them for careers in the renewable energy sector and contribute to advancements in sustainable energy solutions.
The relevance of this project extends to potential applications in innovative research methods, simulations, and data analysis within educational settings.
By exploring the integration of different controllers and optimization algorithms, researchers can develop new approaches to maximize the efficiency of solar power systems. This project opens up opportunities for further research in the optimization of renewable energy sources and the development of more sustainable technologies.
Researchers, MTech students, and Ph.D. scholars in the field of renewable energy, electrical engineering, and control systems can benefit from the code and literature of this project for their work.
They can use the proposed hybrid MPPT system as a reference for their research on improving solar power system efficiency. By studying the algorithms and methodologies implemented in this project, researchers can build upon the existing framework and enhance their own research endeavors.
In conclusion, the proposed project on maximizing the output of solar power systems through a hybrid MPPT system has the potential to enrich academic research, education, and training in the field of renewable energy. By exploring advanced algorithms and simulation techniques, this project can inspire innovative research methods and contribute to the development of more efficient and sustainable energy solutions. The future scope of this project includes further optimization of the hybrid MPPT system, integration with smart grid technologies, and real-world testing to validate its effectiveness in practical applications.
Algorithms Used
The core algorithms utilized in this project include the MPPT algorithm, P&O method, and the Genetic Algorithm. The MPPT algorithm is designed to optimally use the P&O method and PID controller to efficiently maximize power output. The PID controller is integrated into the system to ensure the required voltage is achieved for optimal performance. The Genetic Algorithm is employed to tune the gain values in the PID controller, enhancing the overall efficiency of the system. By combining these algorithms, the project aims to improve accuracy in power optimization and enhance the efficiency of the system to better meet the project objectives.
Keywords
SEO-optimized keywords: Solar Powered Efficiency, Genetic Algorithm, PID Controller, P&O Controller, MPPT System, Resistance, Power Loss, Voltage, Hybrid System, MATLAB, Case Study, Grid System, Battery Storage, Electric Vehicle Batteries, Dummy Load.
SEO Tags
solar power systems, maximum power point tracking, MPPT system, VI characteristic, power loss, resistance, efficient energy system, solar panels, photovoltaic cells, P&O controller, PID controller, genetic algorithm, voltage optimization, hybrid system, MATLAB software, electric vehicle batteries, battery storage, grid system, case study, power efficiency, solar panel irradiance, dummy load, research project, PhD research, MTech project, research scholar, sustainable energy conversion, power optimization.
| Shipping Cost |
|
No reviews found!














































No comments found for this product. Be the first to comment!