Optimizing Energy Efficiency in Wireless Sensor Networks through TEEN Protocol
Problem Definition
Wireless sensor networks built on IoT present a critical issue concerning energy preservation. The constant data communication in these networks quickly depletes the energy reserves of the sensors, resulting in a shortened lifespan. The existing threshold-based communication model used in these networks triggers communication rounds regardless of the data's significance, leading to unnecessary energy consumption. As a result, there is a pressing need to develop a system that can optimize communication efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and extend the network's longevity. This challenge underscores the importance of exploring new strategies and technologies to address the energy efficiency problem in wireless sensor networks, ultimately enhancing their performance and reliability.
Objective
The objective is to address the energy preservation challenge in IoT wireless sensor networks by developing a more efficient communication model. This will be achieved by introducing the CV factor in root selection and utilizing the TEEN protocol to reduce unnecessary communication rounds and maximize the network's lifespan. The goal is to demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach in improving energy efficiency and prolonging the network's lifetime through performance evaluations and comparisons with traditional methods. The rationale behind selecting the TEEN protocol and implementing the CV factor is their potential to enhance energy preservation and network efficiency by setting specific threshold conditions for communication and optimizing root selection based on sensing value. The use of MATLAB for implementation allows for reliable testing and evaluation under different scenarios, providing valuable insights into the proposed system's effectiveness.
Proposed Work
The proposed work aims to address the energy preservation challenge faced by IoT wireless sensor networks through the development of a more efficient communication model. By introducing the CV factor in root selection and utilizing the TEEN protocol, the project focuses on reducing unnecessary communication rounds and maximizing the network's lifespan. The shift from the traditional HEED protocol to TEEN protocol allows for communication only when specific thresholds are met, leading to energy conservation and improved network efficiency. By evaluating the system's performance under various scenarios and comparing results with traditional methods, the project seeks to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach in enhancing energy efficiency and prolonging the network's lifetime.
The rationale behind choosing the TEEN protocol and introducing the CV factor lies in their potential to significantly improve energy preservation and network efficiency.
By setting specific threshold conditions for communication and basing root selection on sensing value, the proposed approach aims to eliminate unnecessary communication rounds and prolong the network's lifespan. The utilization of MATLAB for software implementation provides a reliable platform for testing and evaluating the proposed system under different scenarios. The evaluation of the system's performance under varying conditions and comparison with traditional methods will provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of the proposed approach, further reinforcing the rationale behind the chosen techniques and algorithms for solving the defined problems.
Application Area for Industry
This project's proposed solutions can be applied across various industrial sectors that rely on wireless sensor networks and IoT technology, such as manufacturing, agriculture, healthcare, and smart buildings. In manufacturing, the implementation of the proposed energy-efficient model can improve the monitoring of production processes while extending the sensors' lifespan. In agriculture, the optimized communication system can enhance crop monitoring, irrigation efficiency, and pest control. In healthcare, the system can assist in remote patient monitoring and emergency response coordination. Lastly, in smart buildings, energy consumption can be accurately monitored, and resources can be efficiently managed to reduce wastage.
The benefits of adopting these solutions include increased operational efficiency, cost savings on sensor maintenance, improved decision-making based on real-time data, and overall sustainability in resource management.
Application Area for Academics
The proposed project focusing on improving energy efficiency in wireless sensor networks through the use of the TEEN protocol can significantly enrich academic research, education, and training in the field of IoT and sensor networks. By addressing the critical issue of energy preservation and network longevity, the project provides a practical application of innovative research methods and simulations.
Researchers in the field of IoT and wireless sensor networks can benefit from the project by exploring new approaches to enhancing network efficiency and performance. The comparison of the traditional HEED protocol with the more efficient TEEN protocol offers valuable insights into the potential benefits of optimizing communication based on data relevance.
MTech students and PHD scholars can utilize the code and literature from this project to further their research and study in wireless sensor networks.
By understanding the implementation and evaluation of the TEEN protocol in a real-world scenario, students can explore the practical implications of energy-efficient communication protocols in IoT devices.
The use of MATLAB software and algorithms such as HEED and TEEN provides a practical framework for conducting experiments, analyzing data, and evaluating network performance. By applying these tools to different test scenarios, researchers and students can gain a comprehensive understanding of the impact of energy-efficient protocols on wireless sensor networks.
Future research opportunities could involve refining the TEEN protocol further, exploring variations in network configurations, and expanding the application of energy-efficient communication protocols to other IoT devices. By continuing to innovate and optimize energy preservation strategies in wireless sensor networks, researchers can contribute to the advancement of IoT technology and improve the sustainability of IoT devices in various applications.
Algorithms Used
Two primary algorithms used in the project are HEED (Hybrid Energy-Efficient Distributed Clustering) and TEEN (Threshold-sensitive Energy Efficient sensor Network) protocols. HEED is traditionally used for cluster formation in sensor networks and communication, while TEEN focuses on energy efficiency by checking for data variations and enabling communication only when necessary.
The project aims to propose a more efficient model for root formation in wireless sensor networks by emphasizing energy preservation. The root selection is based on a newly introduced factor - the sensing value (CV). A shift from HEED to TEEN protocol is made to enhance energy efficiency, where communication occurs only when specific condition thresholds are met.
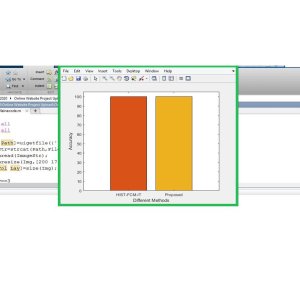
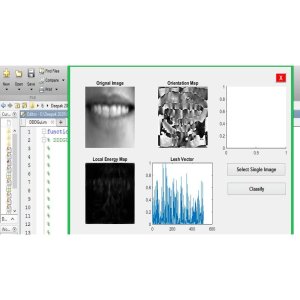
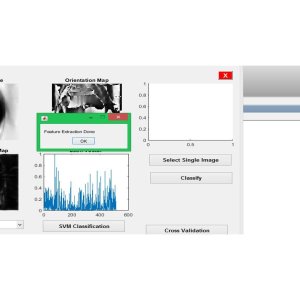
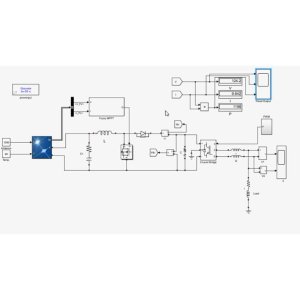
Using MATLAB software, the study evaluates the wireless sensor network's performance and efficiency under various scenarios such as changing area, different sink locations, and varied S vector configurations. The results are compared with traditional methods to assess the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Keywords
SEO-optimized keywords: Wireless Sensor Networks, IoT, Energy Preservation, Network Lifespan, HEED Protocol, TEEN Protocol, Cluster Formation, Root Formation, Sensing Value, Network Parameters, Threshold-based Communication, Sink Location, S Vector, MATLAB, Energy Efficiency, Communication Rounds, Energy Conservation, Sensor Nodes, Energy-efficient Model, Network Performance, Scenario Evaluation, Radical Approach, Energy-efficient Clustering, Wireless Communication, Data Relevance, System Efficiency.
SEO Tags
Wireless Sensor Networks, IoT, Energy Preservation, Network Lifespan, HEED Protocol, TEEN Protocol, Cluster Formation, Root Formation, Sensing Value, Network Parameters, Threshold-based Communication, Sink Location, S Vector, MATLAB, Research Scholar, PHD student, MTech student, Wireless Communication, Sensor Nodes, Energy Efficiency, Data Communication, Network Performance, Energy Conservation, Sensor Network Protocols, Network Simulation, Wireless Communication Systems, IoT Applications, Energy Efficient Protocols, MATLAB Simulation.
| Shipping Cost |
|
No reviews found!














































No comments found for this product. Be the first to comment!