Iterative Channel Equalization Methods for OFDM Systems: A Comparative Analysis of LMS, LMK, and ILMK Algorithms
Problem Definition
In the domain of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) systems, the predominant use of traditional channel equalization techniques such as Zero Forcing (ZF) and Minimum Mean Square Error (MMSE) has been effective in combating channel distortions. However, it is important to acknowledge the inherent limitations associated with these methods. ZF, for example, can suffer from noise amplification in scenarios where channel correlation is high, while MMSE may be sensitive to errors in channel estimation. Despite the promising results demonstrated by ZF and MMSE, there remains a significant gap in exploring alternative channel equalization approaches that can address these shortcomings and potentially deliver superior performance in OFDM systems. Thus, there is a pressing necessity to broaden the scope of research to investigate diverse equalization techniques that offer improved robustness and efficiency in handling the challenges posed by channel distortions in OFDM systems.
Objective
The objective of this project is to address the limited exploration of alternative channel equalization techniques in Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) systems. By conducting a comparative study of Least Mean Square (LMS), Least Mean Kurtosis (LMK), and Improved Least Mean Kurtosis (ILMK) methods, the research aims to evaluate their efficacy in improving communication in OFDM-based Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) systems. The focus is on analyzing the convergence behavior and noise mitigation capabilities of these methods to identify the most suitable channel equalization approach that can optimize the performance and robustness of OFDM systems. Through this study, the goal is to bridge the gap in the existing literature and contribute towards the development of more efficient communication techniques for WSN applications.
Proposed Work
In this project, the problem of limited exploration of alternative channel equalization techniques in Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) systems is addressed through a detailed comparative study of three different methods. The innovative aspect of this research lies in the examination of the efficacy of Least Mean Square (LMS), Least Mean Kurtosis (LMK), and Improved Least Mean Kurtosis (ILMK) for improving communication in OFDM-based Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) systems. By focusing on the convergence behavior and noise mitigation capabilities of each method, this study aims to provide valuable insights into their performance and potential advantages over conventional approaches like Zero Forcing (ZF) and Minimum Mean Square Error (MMSE).
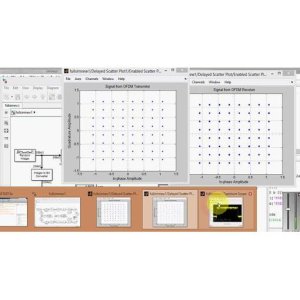
The rationale behind choosing LMS, LMK, and ILMK lies in their potential to overcome the limitations associated with ZF and MMSE, such as noise amplification and sensitivity to channel estimation errors. By evaluating key performance metrics like Mean Standard Deviation (MSD) over iterative processes, the project aims to identify the most suitable channel equalization method that can optimize the performance and robustness of OFDM systems.
Through a systematic analysis and comparison of these methods, the research aims to fill the existing gap in the literature and contribute towards the development of more efficient communication techniques for WSN applications.
Application Area for Industry
This project's proposed solutions can find application in various industrial sectors such as telecommunications, wireless communication, and radar systems. In the telecommunications sector, the utilization of alternative channel equalization methods like LMS, LMK, and ILMK can address the challenges of noise amplification and sensitivity to channel estimation errors commonly encountered in OFDM systems. By implementing these novel equalization techniques, industries can improve the overall performance and robustness of communication systems, leading to enhanced signal quality and reliability. Similarly, in radar systems, the adoption of these advanced equalization methods can help in mitigating channel distortions and improving the accuracy of target detection and tracking.
Furthermore, by broadening the scope of investigation to include diverse equalization methods, industries can benefit from valuable insights into identifying the most suitable channel equalization approach for their specific requirements.
By evaluating the convergence behavior and effectiveness of different equalization methods, organizations can make informed decisions to optimize the performance of their systems and overcome the limitations of conventional equalization techniques. Overall, the implementation of these proposed solutions in various industrial domains can lead to improved efficiency, reliability, and quality of communication and radar systems, ultimately contributing to enhanced overall operational effectiveness.
Application Area for Academics
The proposed project has the potential to greatly enrich academic research, education, and training within the field of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) systems. By exploring alternative channel equalization methods such as Least Mean Square (LMS), Least Mean Kurtosis (LMK), and Improved Least Mean Kurtosis (ILMK), researchers can broaden their understanding of effective techniques for mitigating channel distortions and noise in OFDM systems.
This comparative study offers valuable insights into the convergence behavior and performance of each method, allowing researchers to make informed decisions about the most suitable approach for optimizing the robustness and efficiency of OFDM systems. By examining key performance metrics such as Mean Standard Deviation (MSD) over iterative processes, researchers can assess the effectiveness of each method in real-world scenarios.
The relevance of this project extends to a wide range of technology and research domains within the field of communication systems and signal processing.
Researchers, MTech students, and PhD scholars can leverage the code and literature generated from this study to enhance their own work in developing innovative research methods, simulations, and data analysis techniques within educational settings.
This project opens up opportunities for further exploration and experimentation in the realm of channel equalization methods for OFDM systems. Future research could focus on refining existing algorithms, exploring new techniques, or applying these methods to other communication systems for enhanced performance.Overall, this project holds immense potential for advancing academic research, education, and training in the field of OFDM systems and beyond.
Algorithms Used
The algorithms used in this project are Least Mean Square (LMS), Least Mean Kurtosis (LMK), and Improved Least Mean Kurtosis (ILMK). These algorithms play a crucial role in channel equalization within Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) systems.
The Least Mean Square (LMS) algorithm is a widely used adaptive filter algorithm that minimizes the mean square error between the desired signal and the output of the filter. It helps in reducing noise and distortions in the channel by adjusting filter weights iteratively.
The Least Mean Kurtosis (LMK) algorithm focuses on minimizing the kurtosis of the error signal, aiming to exploit higher-order statistics for improved channel equalization.
By considering the kurtosis, which measures the peakiness of a distribution, LMK can offer enhanced performance in challenging channel conditions.
The Improved Least Mean Kurtosis (ILMK) algorithm builds upon the LMK algorithm by introducing additional enhancements to further improve performance and convergence speed. ILMK aims to provide superior channel equalization capabilities by refining the adaptive filtering process based on kurtosis metrics.
By comparing the performance of these three algorithms using metrics such as Mean Standard Deviation (MSD) over iterative processes, this project seeks to identify the most effective channel equalization method for optimizing the robustness and performance of OFDM systems.
Keywords
SEO-optimized keywords: OFDM systems, channel equalization methods, Zero Forcing, MMSE, LMS, Least Mean Square, LMK, Least Mean Kurtosis, Improved Least Mean Kurtosis, convergence behavior, channel distortions, noise mitigation, Mean Standard Deviation, iterative processes, wireless communication, signal processing, iterative decoding, turbo equalization, iterative algorithms, error correction, channel estimation, interference cancellation, performance evaluation, convergence analysis.
SEO Tags
iterative channel equalization, OFDM systems, performance evaluation, convergence analysis, wireless communication, signal processing, iterative decoding, turbo equalization, iterative algorithms, iterative receiver, error correction, equalization techniques, convergence criteria, channel estimation, interference cancellation, Least Mean Square (LMS), Least Mean Kurtosis (LMK), Improved Least Mean Kurtosis (ILMK), channel distortions, noise mitigation, Mean Standard Deviation (MSD), robustness of OFDM systems
| Shipping Cost |
|
No reviews found!














































No comments found for this product. Be the first to comment!