Watch the complete assembly process in the videos provided below
Video 1 : Assembling the Eye Mechanism for a 3D Printed Humanoid
In this video, we provide a comprehensive guide to assembling the eye mechanism for the humanoid chatbot, detailing each step for optimal functionality and lifelike interaction. The assembly begins with mounting the servo motors, which are responsible for controlling both the movement and blinking of the eyes. You'll learn how to carefully position the servos inside the head structure, ensuring that they are aligned with the 3D-printed eye sockets for fluid horizontal and vertical eye movement.
By the end of this section, you'll have a fully assembled and responsive eye mechanism, ready to bring your humanoid chatbot to life with natural, human-like gestures and expressions.
Video 2 : Assembling the Neck Mechanism for Realistic Head Movements
In this video, we take you through the complete process of assembling the neck mechanism for the 3D-printed humanoid, focusing on achieving realistic head movements. The assembly starts with attaching the servo motor to the neck joint, which is the core component responsible for controlling the head's rotational movements. You'll see how to properly position the motor within the neck framework to allow smooth and natural motion.
By the end of this section, your humanoid’s neck mechanism will be fully assembled and optimized for lifelike, dynamic head movements, making the interactions with your humanoid appear more natural and engaging.
Video 3 : Assembling the Jaw and Face for Speech Simulation
In this video, we walk you through the detailed assembly of the jaw and face mechanism for realistic speech simulation in the 3D-printed humanoid. The process begins with attaching the servo motors responsible for controlling the jaw's movement. You'll see how to carefully position and secure the servos inside the 3D-printed face structure, ensuring they are properly aligned to enable precise jaw motion, which is critical for simulating speech patterns.
By the end of this section, the jaw and face assembly will be fully operational, laying the groundwork for realistic speech simulation. With the servos and jaw mechanism correctly installed and calibrated, your humanoid will be ready to simulate talking, enhancing its lifelike interaction capabilities.
Objectives
The primary objective of this project is to create an AI-powered humanoid chatbot that can simulate human-like interactions through a 3D-printed face. This involves developing a system that not only processes and responds to user queries but also visually represents these responses through facial movements. By integrating advanced AI algorithms with precise motor control, the project aims to enhance human-robot interaction, making it more engaging and lifelike. Additionally, this project seeks to explore the practical applications of combining AI with 3D printing and microcontroller technology, demonstrating their potential in educational, assistive, and entertainment contexts.
Key Features
- AI Integration: Utilizes advanced AI to understand and respond to user queries.
- 3D Printed Face: A realistic face that can express emotions through movements.
- Servo Motor Control: Precisely controls eye blinking, mouth movements, and neck rotations.
- ESP32 Microcontroller: Manages motor control and Wi-Fi communication.
- Embedded C and Python: Dual programming approach for efficient motor control and AI functionalities.
- Wi-Fi Connectivity: Sends and receives data from an AI server to process queries.
- Stable Power Supply: A 5V 10A SMPS ensures all components receive consistent power.
Application Areas
This AI-powered 3D printed humanoid chatbot has diverse applications:
- Education: Acts as an interactive tutor, helping students with queries in a lifelike manner.
- Healthcare: Provides companionship and basic assistance to patients, particularly in elder care.
- Customer Service: Serves as a front-line customer service representative in retail and hospitality.
- Entertainment: Functions as a novel and engaging entertainer in theme parks or events.
- Research and Development: Used in R&D to explore advanced human-robot interaction and AI capabilities.
- Marketing: Attracts and interacts with potential customers at trade shows and exhibitions.
Detailed Working
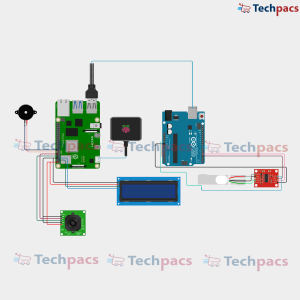
The AI-powered 3D printed humanoid chatbot operates through a combination of hardware and software components. The 3D-printed face is equipped with servo motors that control the eyes, mouth, and neck. The ESP32 microcontroller, programmed with Embedded C, handles the motor movements. When a user asks a question, the ESP32 sends this query via Wi-Fi to an AI server, where it is processed using Python. The server's response is then transmitted back to the ESP32, which controls the servo motors to mimic speaking by moving the mouth in sync with the audio output. The eyes blink, and the neck rotates to enhance the lifelike interaction. A 5V 10A SMPS provides a stable power supply to ensure seamless operation of all components.
Modules Used
- ESP32: Central microcontroller that handles communication and motor control.
- Servo Motors: Control the movements of the eyes, mouth, and neck.
- 5V 10A SMPS: Provides stable power to the ESP32 and servo motors.
- 3D Printed Face: Acts as the physical interface for human-like interactions.
- AI Server: Processes user queries and generates responses.
Summary
The AI-powered 3D printed humanoid chatbot is a sophisticated project that merges AI technology with robotics to create a lifelike interactive experience. Using an ESP32 microcontroller and servo motors, the 3D-printed face can perform a range of expressions and movements. Python-based AI processes user queries, while Embedded C ensures precise motor control. This project has wide-ranging applications in education, healthcare, customer service, entertainment, and beyond. The stable power supply ensures reliable performance, making this an ideal platform for exploring advanced human-robot interactions. We offer customizable solutions to meet specific needs, ensuring the best performance at the best cost.
Technology Domains
- Artificial Intelligence
- Robotics
- Microcontroller Programming
- 3D Printing
- Embedded Systems
Technology Sub Domains
- Natural Language Processing
- Servo Motor Control
- Embedded C Programming
- Python Scripting
- Wi-Fi Communication
| Shipping Cost |
|
No reviews found!






























































No comments found for this product. Be the first to comment!