Advancing Wireless Sensor Networks Through Intelligent Multi-Hop Routing and Fuzzy Decision-Making for Cluster Head Selection
Problem Definition
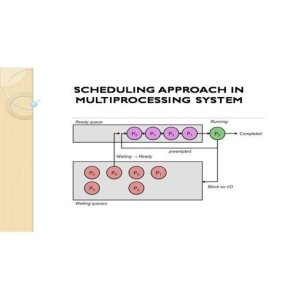
The literature review highlights various drawbacks and limitations of conventional routing protocols, particularly the popular LEACH model, in wireless sensor networks. One of the key issues observed is the high energy consumption resulting from cluster heads needing to travel greater distances, leading to a shorter network lifespan. Additionally, the selection of cluster heads using fuzzy inference systems only considers limited parameters, neglecting other factors that can impact network performance. Moreover, the direct communication of non-cluster nodes with the base station further exacerbates energy usage. These shortcomings underscore the urgent need to enhance existing protocols to improve network efficiency, stability, and longevity.
By addressing these flaws, it is possible to optimize energy utilization and prolong the overall lifespan of wireless sensor networks.
Objective
The objective of the project is to design an energy-efficient protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) that addresses the shortcomings of conventional routing protocols, such as the popular LEACH model. The project aims to improve network efficiency, stability, and longevity by implementing a multi-hop routing approach within each cluster to reduce energy consumption. Additionally, the project will focus on enhancing the cluster head selection process using an extended fuzzy logic input parameter and a fuzzy decision model considering key parameters of sensor nodes. By implementing a relay mechanism for data transmission from sensor nodes to the base station via neighboring nodes and cluster heads, the project seeks to minimize energy usage and optimize the overall lifespan of WSNs.
Proposed Work
In this project, we have identified a gap in the existing literature regarding the inefficiencies of conventional routing protocols in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs). The current protocols, such as the LEACH model, suffer from high energy consumption due to the selection of cluster heads and direct communication with the base station. To address this issue, the objective of our project is to design an energy-efficient protocol based on an extended fuzzy logic input parameter for cluster head selection in WSNs. Our proposed work involves implementing a multi-hop routing approach within each cluster to reduce the distance that cluster heads need to travel, thus conserving energy and extending the network lifespan. Additionally, a fuzzy decision model considering key parameters of sensor nodes will be used for effective cluster head selection.
By implementing a relay mechanism for data transmission from sensor nodes to the base station via neighboring nodes and cluster heads, energy consumption will be minimized, leading to a more stable and efficient network. Our rationale for choosing these techniques lies in their ability to address the drawbacks of existing protocols and improve the overall performance of WSNs in terms of energy efficiency and network lifespan.
Application Area for Industry
This project's proposed solutions can be applied in various industrial sectors such as Smart Manufacturing, Agriculture, Environmental Monitoring, and Healthcare. In Smart Manufacturing, the implementation of the multi-hop routing approach can optimize energy consumption and enhance the network lifespan of wireless sensor networks used for monitoring and controlling manufacturing processes. In Agriculture, the use of the fuzzy decision model for cluster head selection can improve communication efficiency and prolong the network lifetime in applications like precision agriculture and irrigation management. In Environmental Monitoring, the utilization of multi-hop communication can reduce energy consumption in remote sensor networks monitoring air quality, water levels, and wildlife habitats. Lastly, in Healthcare, the incorporation of the proposed mechanisms can lead to improved data transmission efficiency and increased network stability in patient monitoring systems and medical device networks.
By addressing the specific challenges of energy consumption and network lifespan in various industrial domains, this project provides benefits such as improved operational efficiency, prolonged network lifetime, and enhanced data transmission reliability.
Application Area for Academics
The proposed project aims to enrich academic research, education, and training in the field of wireless sensor networks (WSN) by addressing the limitations of existing protocols and proposing an enhanced approach. By implementing multi-hop routing and a fuzzy decision model for cluster head selection, the project offers a more energy-efficient and reliable solution for WSNs, ultimately leading to extended network lifespan.
Researchers in the field of WSNs can benefit from this project by exploring innovative research methods and simulations using the proposed algorithms. They can use the code and literature of this project as a reference for their work, conducting further experiments and analysis to advance the current understanding of WSN protocols and performance optimization.
MTech students and PhD scholars can also utilize the proposed project for their academic studies, gaining practical insights into network protocols, data analysis, and optimization strategies.
By studying the proposed algorithms and implementing them in real-world scenarios, students can enhance their research skills and contribute to the development of more efficient WSN solutions.
In terms of future scope, the project opens up possibilities for exploring new technologies and research domains in the field of WSNs. Researchers can further refine the fuzzy decision model, explore additional parameters for cluster head selection, and investigate the impact of multi-hop routing on network performance. By building upon the foundation laid out in this project, academics can continue to push the boundaries of WSN research and education, paving the way for more innovative and sustainable network solutions.
Algorithms Used
Fuzzy Logic is used in the proposed work to enhance the communication efficiency in cluster-based wireless sensor networks. The algorithm helps in selecting the cluster head (CH) based on four important parameters of sensor nodes: average distance of neighbor node, residual energy, moving speed, and pause time. By using fuzzy decision model, the CH selection process is optimized, leading to improved network performance and energy conservation.
Additionally, the proposed approach implements multi-hop routing within each cluster, where sensor nodes communicate with each other over shorter distances before sending data to the base station. This minimizes the energy consumption of CH nodes and extends the network lifespan by reducing the distance traveled for data transmission.
Moreover, a mechanism is introduced to relay data from sensor nodes outside the cluster to the CH, further minimizing energy consumption and enhancing network efficiency.
Keywords
SEO-optimized keywords: Mobile Sensor Networks, Clustering, Hierarchical clustering, Enhanced clustering, Fuzzy Inference Systems, Fuzzy logic, Data aggregation, Mobile nodes, Data fusion, Energy efficiency, Network lifetime, Data management, Data routing, Mobile communication, Self-organization, Wireless communication, Network performance, Artificial intelligence, Multi-hop routing, Sensor nodes, CH selection, Residual energy, Moving speed, Pause time, Network stability, Protocol efficiency.
SEO Tags
mobile sensor networks, clustering, hierarchical clustering, enhanced clustering, fuzzy inference systems, fuzzy logic, data aggregation, mobile nodes, data fusion, energy efficiency, network lifetime, data management, data routing, mobile communication, self-organization, wireless communication, network performance, artificial intelligence, LEACH protocol, multi-hop routing, sensor nodes, base station, cluster head selection, fuzzy decision model, energy conservation, research methodology, literature review, WSN protocols, research challenges, protocol comparison
| Shipping Cost |
|
No reviews found!
















































No comments found for this product. Be the first to comment!